AX Translate App: Getting Started for Translators
TIP
This tutorial is a beta version. If you have any comments, feel free to report them to your CS-Agent or our support via chat. We appreciate your feedback.
Prerequisites for Working with the AX Translate App
To work with the AX Translate App, you need to have
- an invitation for the AX Translate APP (you have to confirm it)
- assigned Translation Packages
What you learn in this tutorial
In this tutorial, you will learn...
- ... how a text generation translation differs from traditional translations.
- ... how the workflow in the Translate App works
- ... which different items are due for translation and how they are characterized.
How does data-to-text generation work?
In the AX NLG cockpit texts are generated automatically based on structured data and a ruleset.
- Upload Structured Data Organized data in relational databases or tables, etc.is the basis for automated text generation.
- Configure Rule Set Users define logics for the data, configure the structure of the text and define phrases - all in their desired style and tonality. On the base of these rules, the software also ensures grammatical correctness.
- Generate Content The finished text is then created from the combination of data and a rule set. This creates a unique text for each data set. The texts can be easily updated and regenerated.
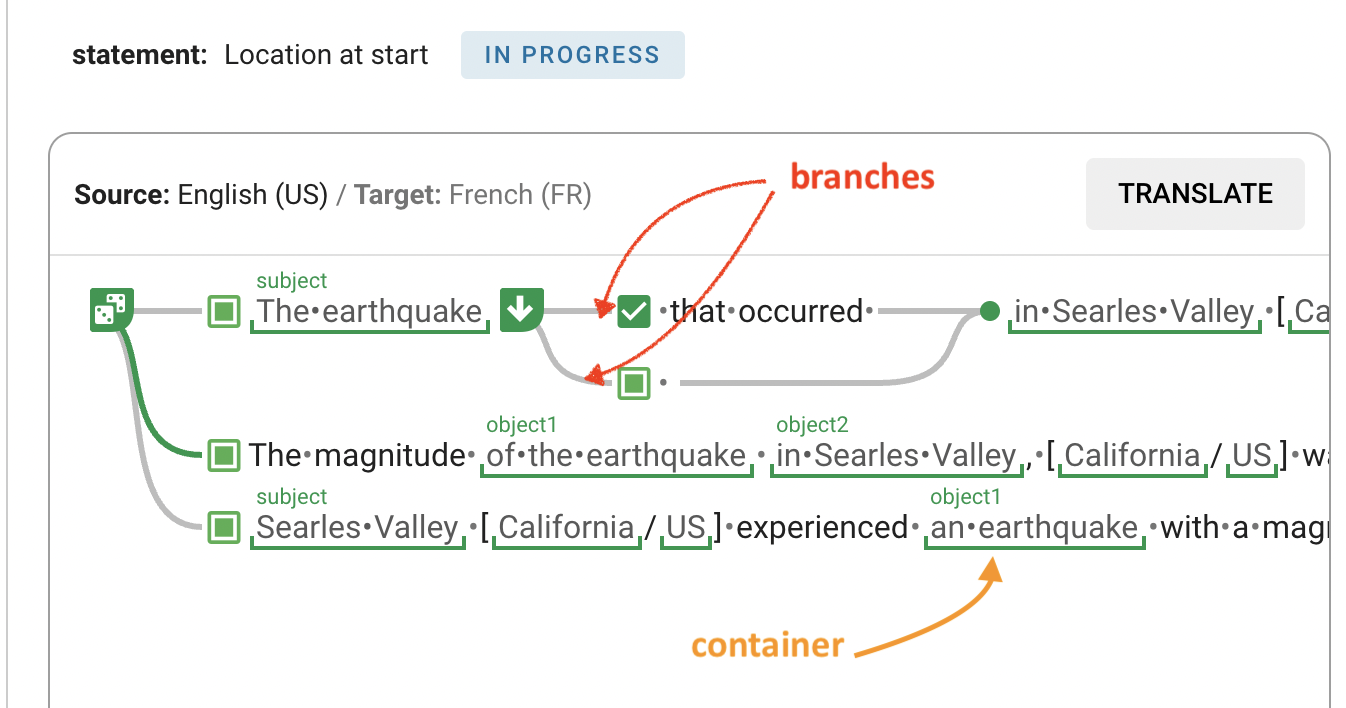
Statements and Containers – Key Concepts of the NLG Platform
A key concept on the NLG platform is the Statement. It is a content and linguistic unit and can include static and variable parts (Containers). Statements can be structured with Branches to provide alternative phrasing.
Containers store necessary information for the correct output of the Statements: Which data should be inserted at this point and also details about the grammar.
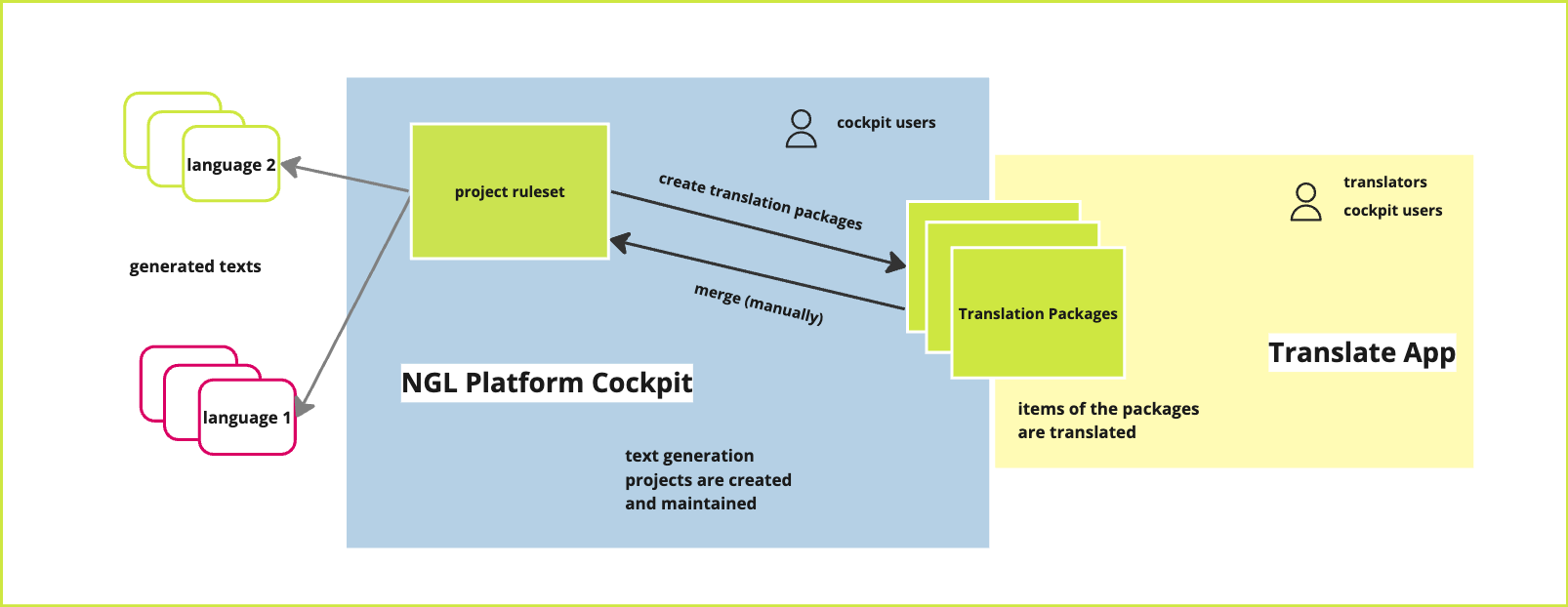
How to translate on the Translate App
In order to be able to perform translation tasks separately, the parts relevant for translation are bundled into translation packages in AX Cockpit. These translation packages can then be accessed from the Translation App.
There are two roles for the translation tasks:
- The Translator works on the Translate App and translate the items.
- The Cockpit User is responsible for the management of the *Translation_Packages_ and works primarily in the AX Cockpit.
The specifics of translating text generation projects
For translation work, it is important to know that text generation does not involve the complete translation of individual texts from the source language to the target language. Rather, it involves the transfer of the data (if it has not already been translated), the set of rules, and its linguistic components into the new language. These components can then be used to generate individual texts in the target language.
Translation for text generation in the Translation app is characterized by two basic principles that distinguish the procedure from common translation:
Translating items, not a continuous text: You're not translating continuous text. You are dealing with multiple elements that need to be translated and, in some cases, annotated with grammatical information.
Translating is based on a specific real data set (Preview Test Object) The translation is carried out on a specific real data set, but it has to work for different data sets as well. This is primarily important when translating statement items consisting of static and variable text, i.e. values derived from data.
One or more preset data sets (Preview Test Objects) are included in the Translation Packages for this purpose. If there is more than one Preview Test Object, you can select one for translation and then check your translation by switching to a different Preview Test Object*.
The Workflow on the Translate App
The dashboard of the application displays all the Translation Packages assigned to you, along with their source and target languages.
- Clicking on a translation package brings up a list of items to be translated.
- You start your work by clicking the Translate Next button and work through the list of items in the translation package from top to bottom.
- The Translate button initiates an automated machine translation, which you then review and improve.
- When you have successfully translated the item, you can mark it as Submitted. If you still have questions, select an option (needs editing or blocked) from the Skip menu and add a comment if necessary.
- Continue through the entire Translation Package.
This is the ideal flow of the items during translation:
- not started: Initial state, nobody has started to translate this item.
- in progress: A translator (you or someone else) has started to work on this item. You can have multiple items in this state.
- submitted: The item is translated and submitted for review by a cockpit user. This is the target state for you as a translator
- in review: A cockpit user is currently reviewing this item. It is read-only now.
- merged: This item is merged into the source project in the cockpit. This state cannot be altered.
If there are still issues to be resolved for the translation of an item, you can assign the following states:
- needs editing: Marks the items as needs editing from you (or other translators). Look out for comments.
- blocked:: Item is unresolvable from you (or other translators). Request for help from a cockpit user.
For an overview of all possible workflows and item states, see the General Documentation.
Types of translate items & what you need to know for translation
The item types refer to functional elements on the NLG platform. There are four types:
- Statement
- Phrase
- Lookup table entry
- Lexicon entry
The main item types are Statement items with Branches and Containers. Data Content in Containers usually does not need to be translated. In most cases, the data is already available in the target language, or it is transferred via Lookup tables, i.e. it has already been translated elsewhere.
However, it is useful to check the grammatical information in the Containers of the target language, because there may be discrepancies between the necessary grammatical information of the source and the target language.
The two items Lookup table entry and Phrase are handled in the same way in the Translate App. The task here is to transfer the basic forms in the tables of the source language into the basic form of the target language.
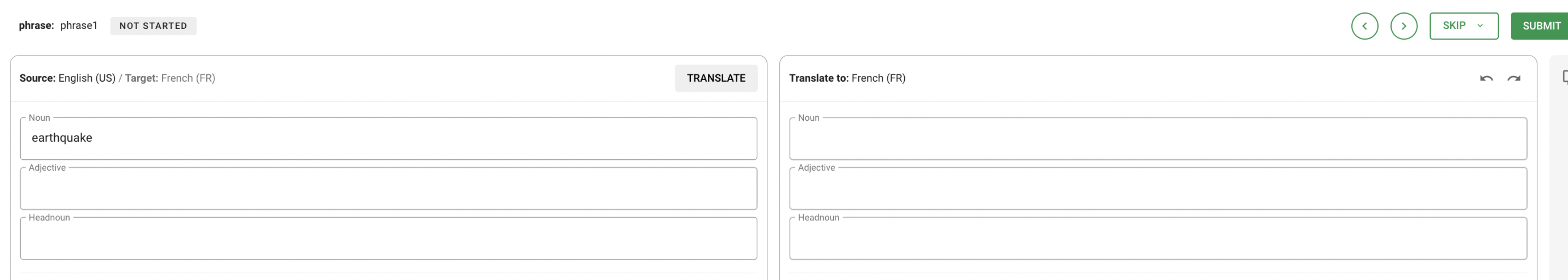
TIP
In linguistics a "head" is the keyword that determines the nature of a phrase (in contrast to any modifiers or determiners).
Lexicon entry items are a special case in that they are not items that need to be translated, but are forms where grammatical information about a word is entered.***
![]()
3 Tips for a good workflow on the Translate App
Go through the entries in the order they appear (">" takes you to the next entry), and skip them if you get stuck on something. Following the order ensures that the items are translated in a meaningful sequence. For example, in some cases, you may need a translation of a Lookup table entry first, which is then used in later statements.
When you are done with a statement, change the Preview Test object to check if the translation also works with different data sets.
Use the comment function to communicate with your AX Cockpit project manager. This way you can clear up ambiguities or get additional information that will make your work easier.
What to do next?
Do you want to get started right away? Log in. You can always get help from AX Support via chat.
Do you want to read up on things: Go to the Translate App Reference Documentation
